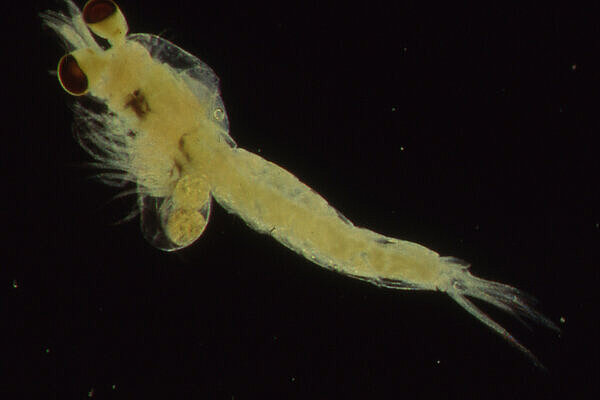
Marine zooplankton
What is marine zooplankton?
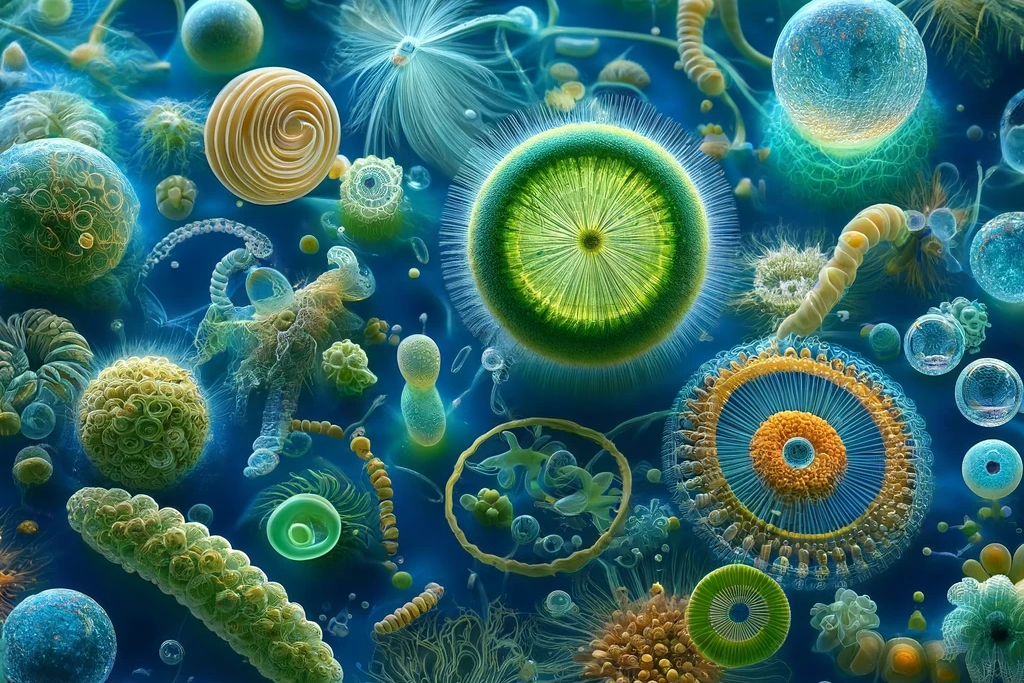
Marine zooplankton is the collective term for all small animals that float or swim in seawater. These include, for example, crustaceans, worms, jellyfish, snails and many more. Marine zooplankton is an important food source for many larger marine animals such as fish, whales and seals.
Marine zooplankton is also known as a superfood because it contains many valuable nutrients. It is rich in proteins, fatty acids, vitamins, minerals and antioxidants. These can help your dog stay healthy and fit.
What are the benefits of marine zooplankton for your dog?
Marine zooplankton can offer your dog many benefits, for example:
- It supports your dog's digestion and immune system by improving gut flora and reducing inflammation.
- It promotes your dog's skin and coat health by moisturizing and relieving itching.
- Strengthens your dog's bones and joints by regulating calcium and phosphorus levels and preventing osteoarthritis.
- It improves your dog's brain and eye function by protecting nerve cells and preserving vision.
What are the disadvantages of marine zooplankton for your dog?
Marine zooplankton also has some disadvantages that you should consider before feeding it to your dog. For example:
- It can trigger allergies or intolerances if your dog is sensitive to seafood. Therefore, watch out for possible symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting or skin rash.
- It may contain harmful substances such as heavy metals or plastic that come from seawater. These can accumulate in your dog's body and lead to health problems. Therefore, only buy marine zooplankton from controlled sources and in organic quality.
- It can change the taste or smell of your dog if you feed it too often or in too large quantities. Some dogs don't like the smell of fish or are avoided by other dogs. Therefore, dose marine zooplankton sparingly and mix it with other ingredients.
How do you feed marine zooplankton to your dog?
Marine zooplankton is available to buy in various forms, for example as a powder, flakes or pellets. You can give it as a supplement to your dog's normal food or as a treat between meals. The recommended amount depends on the size and weight of your dog. Therefore, always follow the instructions on the packaging.
Marine zooplankton is a healthy and sustainable ingredient for your dog that has many health benefits. However, you should also be aware of the possible disadvantages and only feed marine zooplankton in moderation.
Properties 5
Are you looking for other ingredients with a specific property?
Just click on them to find more.
If you notice any signs of hypersensitivity or poisoning in your dog, you should see your vet immediately. We are not a substitute for a vet, but we try to be as accurate as possible. Every dog reacts differently and we recommend you get a second opinion or consult your vet if in doubt.
Stay healthy and take good care of your four-legged friend!😊
Similar to Marine zooplankton
Spirulina is a blue-green algae that is one of the oldest living organisms on earth. It is found in salty lakes and waters and can feed itself through photosynthesis. Spirulina has a spiral...
Chlorella is a freshwater microalgae that is one of the oldest living organisms on earth. It has a high content of chlorophyll, the green pigment in plants that is responsible for photosynthesis....
Phytoplankton consists of microscopic, photosynthetic organisms that live in salty and fresh waters. These plant plankton species are responsible for a significant proportion of the Earth's oxygen...
Krill is a term for various species of small crustaceans that live in large shoals in the cold waters of the Antarctic and North Atlantic. They feed mainly on phytoplankton and are an important food...